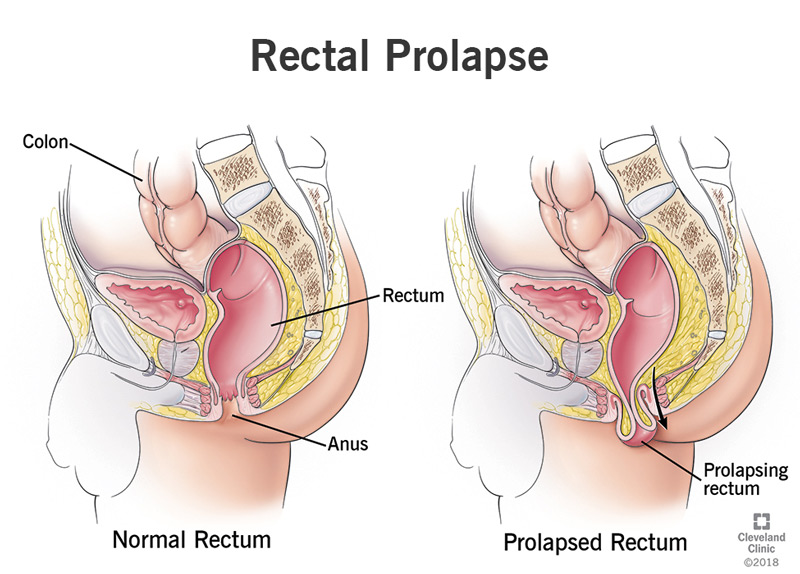
Rectal prolapse, a condition where the rectum protrudes through the anus, can cause significant discomfort and affect daily activities. It affects a large portion of the population, especially women over 50 and those who have had multiple vaginal deliveries. Rectal prolapse can mimic conditions like hemorrhoids or rectal intussusception, making accurate diagnosis crucial. A colonoscopy can detect rectal prolapse and differentiate it from other conditions. While rectal prolapse is not typically an emergency, leaving it untreated can lead to complications such as chronic discomfort, bleeding, and fecal incontinence. Understanding the severity of rectal prolapse and seeking timely treatment is essential to prevent these issues.
The duration of rectal prolapse varies depending on the severity and lifestyle factors. Mild cases may be managed with proper care and lifestyle adjustments, while more severe cases might require medical intervention. Without treatment, rectal prolapse can persist and worsen over time. Severe rectal prolapse is characterized by significant discomfort, chronic pain, and potential complications. Untreated rectal prolapse can lead to chronic pain, persistent bleeding, and infections.
Symptoms
Worst Symptoms of Rectal Prolapse:
- Severe discomfort and pain
- Chronic bleeding
- Fecal incontinence
Symptoms Distinguishing Internal from External Rectal Prolapse:
- Internal Rectal Prolapse: Protrusion of the rectum inside the anal canal
- External Rectal Prolapse: Visible protrusion of the rectum outside the anus
Early Signs of Rectal Prolapse:
- Feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation
- Mucus discharge
- A sensation of a bulge or mass protruding from the anus
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes of Rectal Prolapse:
- Chronic constipation and straining during bowel movements
- Weakness in the pelvic floor muscles
- Multiple vaginal deliveries
- Conditions like cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Can Rectal Prolapse Heal on Its Own? Mild cases of rectal prolapse may improve with lifestyle changes and proper management. However, more severe cases typically require medical or surgical intervention to prevent complications.
Is it Okay to Live with Rectal Prolapse? Living with rectal prolapse without seeking treatment is not recommended. While mild symptoms may be manageable, untreated rectal prolapse can lead to chronic discomfort, persistent bleeding, and fecal incontinence. Seeking appropriate treatment is crucial to improve quality of life and prevent further complications.
Treatment Options for Rectal Prolapse
Dietary Options
- Reduces straining during bowel movements
- Improves bowel regularity
- Supports overall digestive health
Symptoms can improve within a few weeks of starting the diet, but ongoing commitment is necessary.
Medications
Medications can help manage specific symptoms of rectal prolapse. These may include stool softeners to reduce straining and other medications prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Alleviates symptoms such as constipation and straining
- Helps maintain regular bowel movements
- Reduces discomfort associated with rectal prolapse
Improvement can be seen within days to weeks, depending on the medication and individual response.
Rectopexy
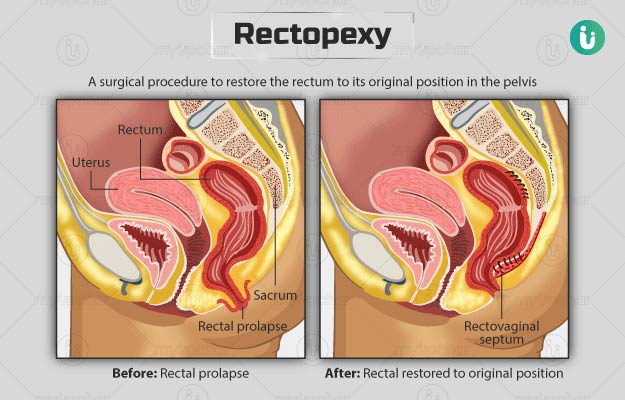
This procedure combines rectopexy with the removal of a portion of the rectum or sigmoid colon. The prolapsed section is resected, and the remaining rectum is secured to the sacrum. This approach is often used when there is associated redundant bowel or severe constipation.
- Comprehensive Treatment: Addresses both the prolapse and any redundant or diseased bowel tissue.
- Improves Bowel Function: Helps relieve symptoms such as chronic constipation and incontinence.
- High Success Rate: Effective in preventing recurrence and restoring normal bowel function.
- Hospital Stay: Typically requires a hospital stay of 5-7 days.
- Full Recovery: Full recovery can take several weeks, with patients gradually increasing their activity levels and following a specific dietary plan. Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor healing and ensure long-term success.
Perineal Rectosigmoidectomy
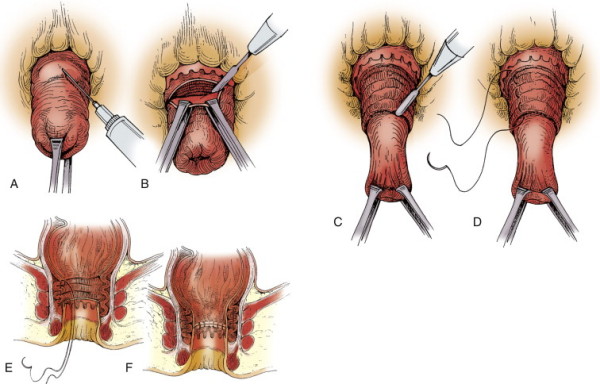
This surgery involves removing the prolapsed section of the rectum through an incision made in the perineum (the area between the anus and the scrotum or vulva). The remaining rectum is then sutured to the surrounding tissues to secure it in place. This approach is often used for older or less fit patients due to its less invasive nature compared to abdominal procedures.
- Effective Treatment: Removes the prolapsed tissue and secures the rectum, reducing the risk of recurrence.
- Less Invasive: The perineal approach is generally less invasive, leading to shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
- Suitable for High-Risk Patients: Ideal for patients who may not be candidates for more extensive abdominal surgery.
- Hospital Stay: Typically requires a hospital stay of 3-5 days.
- Full Recovery: Patients can expect to recover within a few weeks, with gradual return to normal activities. Follow-up visits are necessary to monitor healing and ensure the success of the procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A hemorrhoid can appear as a sudden onset painful lump that may be red, angry, and inflamed. Hemorrhoids can cause discomfort, swelling, rectal pain, anal discharge, and itching or irritation of the anus. These signs of hemorrhoids should not be ignored.
Watch out for these symptoms that may indicate you have hemorrhoids:
- Painful swelling
- Red marble-like growth or lump
- Sharp rectal pain
- Anal discharge
- Irritation and itching
- Rectal bleeding
Usually, symptoms last only a few days and there are plenty of effective ways to treat. Contact us for quick, painless, easy treatment for hemorrhoids – performed in-office. We offer solutions without need for surgery, except in the worst case scenarios.
ColoWell America’s gold standard RUBBER BAND LIGATION – a quick, non-surgical, in-office procedure with little to no pain or complications.
Rubber band ligation is preferred for hemorrhoids because of its effectiveness and affordability compared to other more invasive interventions and non-beneficial over-the-counter remedies.
How the treatment works:
- The treatment targets the blood vessel which feeds the hemorrhoid ligating the blood vessel and cutting off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid.
- The blood flow to the hemorrhoid is interrupted and it begins to shrink.
- Since the hemorrhoid has lost its connection with the feeding vessel, it continues to shrink and fall off during the 3-7 days following treatment.
Affordable, No time off necessary, No hospital visits. No need for special prep before procedure, Performed In Office In Minutes.
Rubber band ligation is the best treatment modality. Complications with banding are little to none. The procedure does not require surgery or a hospital visit, and you don’t have to take off work or require any difficult preparation!
To help prevent hemorrhoids and hemorrhoid recurrence you can eat more high fiber foods, including fruits, vegetables and whole grains. There are also fiber supplements like ColoFlax, Metamucil or Citrucel. Our doctor also recommends daily flax seed powder ingestion (2tbsp/day). You can also help prevent hemorrhoids by drinking four to six glasses of water a day and exercising regularly to help the bowels to move normally.
During pregnancy and delivery hemorrhoids can occur due to anal pressure, constipation, and pushing. Hemorrhoids are also commonly known as piles. It is recommended to eat fiber during pregnancy to avoid constipation, which can lead to hemorrhoidal issues. See a proctologist if you are suffering from hemorrhoids during or after pregnancy.
Internal hemorrhoids that prolapse and protrude can often cause bright red bleeding. Mostly this is painless bleeding seen on the toilet paper with wiping.
External skin tags or External hemorrhoidal tissue usually doesn’t cause bleeding. These external hemorrhoids can cause itching and problems with hygiene.
While hemorrhoids may not be cured with topical treatment, symptomatic relief from pain and itching can be obtained with over-the-counter creams such as Preparation H and Lidocaine, or prescriptions medications like Nifedipine cream.
Thrombosed hemorrhoids are blood clots in a hemorrhoid. This can result in itching around your anus, bleeding when you have a bowel movement, and swelling or lumps around the anus.
There are many causes of thrombosed hemorrhoids, including excessive straining with bowel movement when constipated, diarrhea, abnormal and irregular bowel movements, pregnancy and postpartum state, and prolonged sitting (for example, during travel, working at a desk, etc.)
We use rubber band ligation (RBL) as our standard for hemorrhoid surgery. The doctor places a small rubber band at the base of the hemorrhoid, which in result stops the blood supply and causes the hemorrhoid to shrink and fall off. A hemorrhoidectomy is another choice for hemorrhoid surgery. The procedure removes the hemorrhoid, blood clot and blood vessels. You may get partial anesthesia during this procedure and a hemorrhoidectomy is only performed for the most severe hemorrhoid cases.
How to treat hemorrhoids is based on a patient’s individual condition. Most cases require one to three appointments to prevent recurrence.
Many patients ask us: “Will the hemorrhoids go away on their own?”
The answer lies in the lifestyle choices you make following treatment.
Make FIBER a daily part of your diet. “Ground flax seed is an excellent source of fiber!” – Shiraz Farooq, MD
- Choose a plant-based diet to avoid constipation
- Be sure to drink four to six glasses of water throughout the day
- Avoid strenuous activities
Yes! Contact us to verify your eligibility for services. We also offer Self-Pay rates.
Submit your Suggestion





